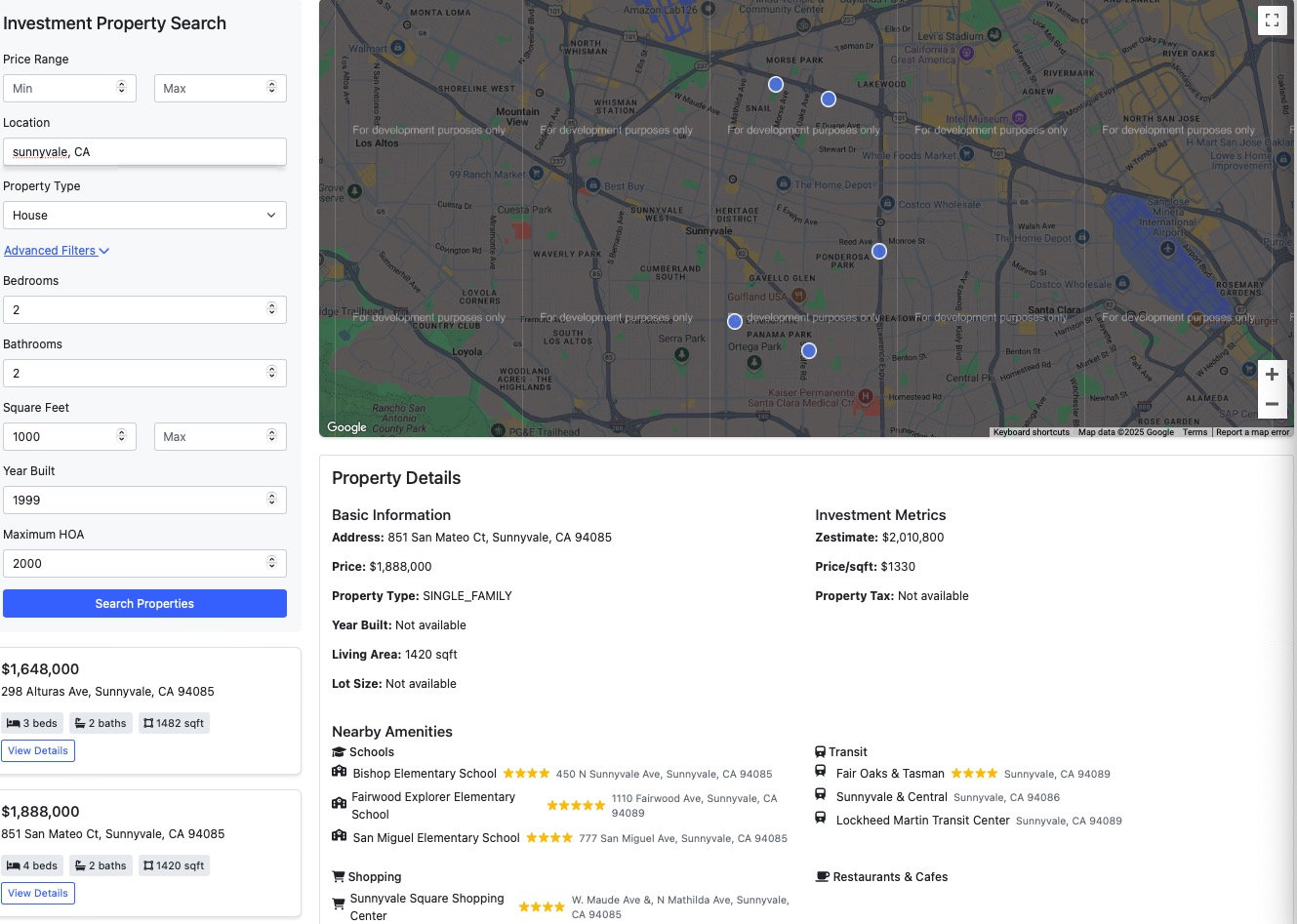
[100-Day AI bootcamp] Day 22: Movie Recommendation and Sentiment Analysis Web App
![[100-Day AI bootcamp] Day 22: Movie Recommendation and Sentiment Analysis Web App](https://growgrow.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/media/blog_images/4151736154176_.pic.jpg)
Developing a personalized movie recommendation app is an exciting project that combines web development, database management, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML). This guide will walk you through the process of creating an AI-driven movie recommendation system that not only suggests movies but also provides detailed information, sentiment analysis from social media, and dynamic user interaction.
The Evolution of Movie Recommendation Systems
The journey of movie recommendations has evolved remarkably over the years:
-
Early Days (1920s-1970s):
- Manual Curation: Recommendations were provided by movie theater owners and critics.
- Film Guides: Publications like Leonard Maltin's Movie Guide became essential for movie enthusiasts.
- Word of Mouth: Personal suggestions were the primary way people discovered new films.
-
Video Store Era (1980s-1990s):
- Clerks as Recommenders: Knowledgeable staff at video rental stores offered personalized suggestions.
- Genre Sections: Physical organization of movies by genre helped users explore different categories.
-
Digital Revolution (2000s):
- Algorithmic Recommendations: Platforms like Netflix introduced algorithms to suggest movies based on user activity.
- Collaborative Filtering: Early models used user ratings to predict preferences.
-
Modern AI Era (2010s-Present):
- Advanced AI and ML Models: Deep learning models analyze vast amounts of data for accurate recommendations.
- Real-Time Personalization: Systems adjust recommendations instantly based on user interactions.
- Multi-Modal Analysis: Incorporation of text, audio, and visual data for comprehensive understanding.
Project Overview
Our goal is to build a full-fledged movie recommendation application with the following features:
- User Interface: A responsive front-end where users can browse movies, receive recommendations, and access detailed information.
- Movie Database: Storage of movie information, including titles, years, genres, and associated news articles with sentiment scores.
- User Authentication: Secure user registration and login system.
- User Interactions: Users can rate movies, which will influence their personalized recommendations.
- Social Media Integration: Fetching tweets related to movies for sentiment and topic analysis.
- Recommendation Engine: An AI-powered system that suggests movies based on user ratings and behavior.
Setting Up the Development Environment
Before we dive into coding, let's set up our development environment.
Technologies Used:
- Front-End: React.js for the user interface.
- Back-End: Flask (Python) for the server-side logic.
- Database: PostgreSQL for data storage.
- Machine Learning: Libraries like scikit-learn, Surprise for collaborative filtering, and NLP tools for sentiment analysis.
- APIs: The Movie Database (TMDb) API, NewsAPI, and X (formerly Twitter) API.
1. Designing the Database System
a. Database Schema
We'll use PostgreSQL and SQLAlchemy ORM for managing our database.
Entities and Relationships:
- Users: Stores user information with secure password hashing.
- Movies: Contains movie details like title, year, and genre.
- UserRatings: Records the ratings given by users to movies.
- NewsArticles: Stores news articles related to movies along with sentiment scores.
- Tweets: Contains tweets about movies for analysis.
Entity-Relationship Diagram:
erDiagram
USER ||--o{ USERRATING : rates
MOVIE ||--o{ USERRATING : is_rated_by
MOVIE ||--o{ NEWSARTICLE : has
MOVIE ||--o{ TWEET : has
USER {
int user_id PK
string username
string password_hash
}
MOVIE {
int movie_id PK
string title
int year
string genre
}
USERRATING {
int user_id PK FK
int movie_id PK FK
float rating
}
NEWSARTICLE {
int article_id PK
int movie_id FK
string title
text body
float sentiment_score
}
TWEET {
int tweet_id PK
int movie_id FK
text content
float sentiment_score
}
b. Implementing Database Models
Install Dependencies:
pip install sqlalchemy psycopg2-binary
Define Models (
models.py
):
from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String, Float, Text, ForeignKey, UniqueConstraint
from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship, declarative_base
Base = declarative_base()
class User(Base):
__tablename__ = 'users'
user_id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
username = Column(String(50), unique=True, nullable=False)
password_hash = Column(String(128), nullable=False)
ratings = relationship('UserRating', back_populates='user')
class Movie(Base):
__tablename__ = 'movies'
movie_id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
title = Column(String(200), nullable=False)
year = Column(Integer)
genre = Column(String(100))
ratings = relationship('UserRating', back_populates='movie')
news_articles = relationship('NewsArticle', back_populates='movie')
tweets = relationship('Tweet', back_populates='movie')
class UserRating(Base):
__tablename__ = 'user_ratings'
__table_args__ = (UniqueConstraint('user_id', 'movie_id', name='user_movie_uc'),)
user_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('users.user_id'), primary_key=True)
movie_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('movies.movie_id'), primary_key=True)
rating = Column(Float, nullable=False)
user = relationship('User', back_populates='ratings')
movie = relationship('Movie', back_populates='ratings')
class NewsArticle(Base):
__tablename__ = 'news_articles'
article_id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
movie_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('movies.movie_id'), nullable=False)
title = Column(String(200), nullable=False)
body = Column(Text, nullable=False)
sentiment_score = Column(Float)
movie = relationship('Movie', back_populates='news_articles')
class Tweet(Base):
__tablename__ = 'tweets'
tweet_id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
movie_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('movies.movie_id'), nullable=False)
content = Column(Text, nullable=False)
sentiment_score = Column(Float)
movie = relationship('Movie', back_populates='tweets')
Create Tables:
# create_tables.py
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from models import Base
engine = create_engine('postgresql://username:password@localhost/moviedb')
Base.metadata.create_all(engine)
Run the script:
python create_tables.py
2. Developing the Back-End with Flask
a. User Authentication
Install Dependencies:
pip install flask flask-login werkzeug
Implement Authentication (
app.py
):
from flask import Flask, render_template, redirect, url_for, request, flash
from flask_login import LoginManager, login_user, login_required, logout_user, UserMixin, current_user
from werkzeug.security import generate_password_hash, check_password_hash
from models import User, engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
app = Flask(__name__)
app.secret_key = 'your_secret_key'
login_manager = LoginManager()
login_manager.init_app(app)
DBSession = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
db_session = DBSession()
@login_manager.user_loader
def load_user(user_id):
return db_session.query(User).get(int(user_id))
class User(UserMixin, User):
pass
@app.route('/register', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def register():
# Registration logic
...
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def login():
# Login logic
...
b. Storing User Ratings
Endpoint to Receive Ratings:
@app.route('/api/rate', methods=['POST'])
@login_required
def rate_movie():
data = request.get_json()
movie_id = data['movie_id']
rating = data['rating']
existing_rating = db_session.query(UserRating).filter_by(user_id=current_user.user_id, movie_id=movie_id).first()
if existing_rating:
existing_rating.rating = rating
else:
new_rating = UserRating(user_id=current_user.user_id, movie_id=movie_id, rating=rating)
db_session.add(new_rating)
db_session.commit()
return jsonify({'success': True}), 200
3. Fetching and Storing Movie Data and News Articles
a. Fetching Movie Information
Fetch Movies from TMDb:
# fetch_movies.py
import requests
from models import Movie, engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
DBSession = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
db_session = DBSession()
def fetch_and_store_movies():
api_key = 'YOUR_TMDB_API_KEY'
response = requests.get(f'https://api.themoviedb.org/3/movie/popular?api_key={api_key}')
movies = response.json().get('results', [])
for m in movies:
movie = Movie(
movie_id=m['id'],
title=m['title'],
year=int(m['release_date'][:4]) if m.get('release_date') else None,
genre=','.join([str(genre_id) for genre_id in m.get('genre_ids', [])])
)
db_session.merge(movie)
db_session.commit()
if __name__ == '__main__':
fetch_and_store_movies()
b. Fetching News Articles
Fetch News and Analyze Sentiment:
# fetch_news.py
import requests
from models import NewsArticle, engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from textblob import TextBlob
DBSession = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
db_session = DBSession()
def analyze_sentiment(text):
return TextBlob(text).sentiment.polarity
def fetch_and_store_news():
api_key = 'YOUR_NEWS_API_KEY'
movies = db_session.query(Movie).all()
for movie in movies:
response = requests.get('https://newsapi.org/v2/everything', params={
'q': movie.title,
'apiKey': api_key
})
articles = response.json().get('articles', [])
for a in articles:
sentiment_score = analyze_sentiment(a['description'] or '')
article = NewsArticle(
movie_id=movie.movie_id,
title=a['title'],
body=a['content'],
sentiment_score=sentiment_score
)
db_session.merge(article)
db_session.commit()
if __name__ == '__main__':
fetch_and_store_news()
4. Integrating Social Media Data and Sentiment Analysis
a. Fetching Tweets Using the X API
Set Up Access to the X API:
- Create a developer account on X Developer Platform.
- Obtain API keys and tokens.
Fetch Tweets and Store in Database:
# tweet_fetcher.py
import tweepy
from models import Tweet, engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from textblob import TextBlob
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
DBSession = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
db_session = DBSession()
def analyze_sentiment(text):
return TextBlob(text).sentiment.polarity
def fetch_tweets(movie):
auth = tweepy.OAuth1UserHandler(
os.getenv('X_API_KEY'),
os.getenv('X_API_SECRET'),
os.getenv('X_ACCESS_TOKEN'),
os.getenv('X_ACCESS_TOKEN_SECRET')
)
api = tweepy.API(auth)
tweets = api.search_tweets(q=movie.title, lang='en', count=100)
for t in tweets:
sentiment_score = analyze_sentiment(t.text)
tweet = Tweet(
movie_id=movie.movie_id,
content=t.text,
sentiment_score=sentiment_score
)
db_session.merge(tweet)
db_session.commit()
def fetch_and_store_tweets():
movies = db_session.query(Movie).all()
for movie in movies:
fetch_tweets(movie)
if __name__ == '__main__':
fetch_and_store_tweets()
b. Performing Topic Analysis
Topic Modeling with Gensim:
# topic_modeling.py
from gensim import corpora, models
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from models import Tweet, engine
DBSession = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
db_session = DBSession()
def perform_topic_modeling(movie_id):
tweets = db_session.query(Tweet).filter_by(movie_id=movie_id).all()
texts = [tweet.content.split() for tweet in tweets]
dictionary = corpora.Dictionary(texts)
corpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(text) for text in texts]
lda_model = models.LdaModel(corpus, num_topics=5, id2word=dictionary, passes=15)
topics = lda_model.print_topics(num_words=4)
return topics
5. Building the Recommendation Engine
a. Implementing Collaborative Filtering
Recommendation Algorithm:
# recommendation_engine.py
from surprise import Dataset, Reader, SVD
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from models import UserRating, engine
import pandas as pd
DBSession = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
db_session = DBSession()
def build_recommendation_model():
ratings = db_session.query(UserRating).all()
data = pd.DataFrame([(r.user_id, r.movie_id, r.rating) for r in ratings], columns=['userId', 'movieId', 'rating'])
if data.empty:
return None
reader = Reader(rating_scale=(1, 5))
dataset = Dataset.load_from_df(data[['userId', 'movieId', 'rating']], reader)
trainset = dataset.build_full_trainset()
algo = SVD()
algo.fit(trainset)
return algo
def get_recommendations(user_id, model, n=10):
movies = db_session.query(Movie).all()
rated_movie_ids = db_session.query(UserRating.movie_id).filter_by(user_id=user_id).all()
rated_movie_ids = [m_id for (m_id,) in rated_movie_ids]
predictions = []
for movie in movies:
if movie.movie_id not in rated_movie_ids:
pred = model.predict(user_id, movie.movie_id)
predictions.append((movie, pred.est))
predictions.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
top_n = [movie for (movie, _) in predictions[:n]]
return top_n
b. API Endpoint for Recommendations
@app.route('/api/recommendations')
@login_required
def get_recommendations_api():
model = build_recommendation_model()
if model is None:
return jsonify({'recommendations': []})
recommendations = get_recommendations(current_user.user_id, model)
recommendations_data = [{
'movie_id': movie.movie_id,
'title': movie.title,
'year': movie.year,
'genre': movie.genre
} for movie in recommendations]
return jsonify({'recommendations': recommendations_data})
6. Developing the Front-End with React.js
a. Setting Up the React App
Initialize React Project:
npx create-react-app frontend
Install Dependencies:
cd frontend
npm install axios react-router-dom
b. Creating Components
MovieDetails Component:
// MovieDetails.js
import React, { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
import axios from 'axios';
const MovieDetails = ({ match }) => {
const [movie, setMovie] = useState({});
const movieId = match.params.id;
useEffect(() => {
axios.get(`/api/movies/${movieId}`)
.then(response => {
setMovie(response.data);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Error fetching movie details:', error);
});
}, [movieId]);
return (
<div>
<h1>{movie.title}</h1>
<p>{movie.overview}</p>
{/* Additional components like NewsSection, SentimentAnalysis, SimilarMovies */}
</div>
);
};
export default MovieDetails;
RatingComponent:
// RatingComponent.js
import React from 'react';
import axios from 'axios';
const RatingComponent = ({ movieId }) => {
const handleRating = (ratingValue) => {
axios.post('/api/rate', {
movie_id: movieId,
rating: ratingValue
})
.then(response => {
// Handle success
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Error submitting rating:', error);
});
};
return (
<div>
{[1,2,3,4,5].map(value => (
<button key={value} onClick={() => handleRating(value)}>
{value} Star{value > 1 ? 's' : ''}
</button>
))}
</div>
);
};
export default RatingComponent;
Recommendations Component:
// Recommendations.js
import React, { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
import axios from 'axios';
const Recommendations = () => {
const [movies, setMovies] = useState([]);
useEffect(() => {
axios.get('/api/recommendations')
.then(response => {
setMovies(response.data.recommendations);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Error fetching recommendations:', error);
});
}, []);
return (
<div>
<h2>Your Recommendations</h2>
<ul>
{movies.map(movie => (
<li key={movie.movie_id}>
{movie.title} ({movie.year})
</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
};
export default Recommendations;
App Component with Routing:
// App.js
import React from 'react';
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Route } from 'react-router-dom';
import MovieDetails from './MovieDetails';
import Recommendations from './Recommendations';
const App = () => {
return (
<Router>
<Route path="/movies/:id" component={MovieDetails} />
<Route path="/recommendations" component={Recommendations} />
{/* Other routes like login, register */}
</Router>
);
};
export default App;
7. Enhancing User Experience with Additional Features
a. Displaying News Articles and Sentiment Analysis
NewsSection Component:
// NewsSection.js
import React, { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
import axios from 'axios';
const NewsSection = ({ movieId }) => {
const [articles, setArticles] = useState([]);
useEffect(() => {
axios.get(`/api/movies/${movieId}/news`)
.then(response => {
setArticles(response.data.articles);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Error fetching news:', error);
});
}, [movieId]);
return (
<div>
<h2>Latest News</h2>
<ul>
{articles.map(article => (
<li key={article.article_id}>
<a href={article.url} target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">
{article.title} (Sentiment: {article.sentiment_score.toFixed(2)})
</a>
</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
};
export default NewsSection;
SentimentAnalysis Component:
// SentimentAnalysis.js
import React, { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
import axios from 'axios';
const SentimentAnalysis = ({ movieId }) => {
const [averageSentiment, setAverageSentiment] = useState(0);
useEffect(() => {
axios.get(`/api/movies/${movieId}/tweets`)
.then(response => {
setAverageSentiment(response.data.average_sentiment);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Error fetching sentiment analysis:', error);
});
}, [movieId]);
return (
<div>
<h2>Audience Sentiment</h2>
<p>Average Sentiment Score: {averageSentiment.toFixed(2)}</p>
</div>
);
};
export default SentimentAnalysis;
8. Visualizing the System Architecture
flowchart TD
User -->|Interacts| FrontEnd[React App]
FrontEnd -->|Requests| BackEnd[Flask API]
BackEnd -->|Queries| Database[(PostgreSQL)]
BackEnd -->|Fetches| APIs[TMDb, NewsAPI, X API]
APIs -->|Returns| BackEnd
Database -->|Stores| Data
BackEnd -->|Responds| FrontEnd
FrontEnd -->|Displays| User
9. Security Considerations
- Secure Password Storage: Use strong hashing algorithms (e.g., BCrypt).
- Input Validation: Protect against SQL injection and XSS attacks.
- API Key Management: Store API keys securely using environment variables.
- HTTPS: Implement SSL/TLS encryption for data in transit.
10. Recommended Resources
To deepen your understanding and assist in the implementation, consider these books:
-
"Flask Web Development" by Miguel Grinberg
Purchase on Amazon
A comprehensive guide to building web applications with Flask. -
"React – Up & Running" by Stoyan Stefanov
Purchase on Amazon
An introduction to building dynamic web applications using React. -
"Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow" by Aurélien Géron
Purchase on Amazon
Practical approaches to machine learning and deep learning with Python. -
"Natural Language Processing with Python" by Steven Bird, Ewan Klein, and Edward Loper
Purchase on Amazon
An in-depth look at processing and analyzing text data using Python.
11. References
- Bird, S., Klein, E., & Loper, E. (2009). Natural Language Processing with Python. O'Reilly Media.
- Géron, A. (2019). Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow. O'Reilly Media.
- Grinberg, M. (2018). Flask Web Development. O'Reilly Media.
- Stefanov, S. (2016). React – Up & Running. O'Reilly Media.
- The Movie Database (TMDb) API Documentation. Retrieved from https://developers.themoviedb.or...
- NewsAPI Documentation. Retrieved from https://newsapi.org/docs
- X Developer Platform Documentation. Retrieved from https://developer.twitter.com/en...
- Surprise Library Documentation. Retrieved from http://surpriselib.com/
Key Takeaways
- Holistic Approach: Building a movie recommendation app requires integrating front-end development, back-end logic, database management, and machine learning.
- User Engagement: Allowing users to interact, rate movies, and receive personalized recommendations enhances the user experience.
- Data Integration: Incorporating data from movies, news articles, and social media provides a richer context for recommendations.
- AI and ML: Utilizing machine learning algorithms like collaborative filtering improves recommendation accuracy.
- Scalability and Performance: Designing the system with scalability in mind ensures that the app can handle growing user base and data volume.
- Security: Implementing robust security practices protects user data and maintains trust.
![[100-Day AI bootcamp] Day 8: Financial Data Assistant](https://growgrow.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/media/blog_images/5321738902254_.pic.jpg)
![[100-Day AI bootcamp] Day 32: Flashcard Generator](https://growgrow.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/media/blog_images/4421737105713_.pic.jpg)
![[100-Day AI bootcamp] Day 9: AI Resume Builder](https://growgrow.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/media/blog_images/4231736341062_.pic.jpg)
![[100-Day AI bootcamp] Day 8: AI generated Children book web app](https://growgrow.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/media/blog_images/4221736329152_.pic.jpg)
![[100-Day AI bootcamp] Day 7: Short Text social media App](https://growgrow.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/media/blog_images/4211736248200_.pic.jpg)
![[100-Day AI bootcamp] Day 2: Building a Real-Time Chatroom with Django](https://growgrow.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/media/blog_images/4201736241999_.pic.jpg)
![[100-Day AI bootcamp] Day 1: AI-Powered Blog](https://growgrow.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/media/blog_images/4161736157861_.pic.jpg)
![[100-Day AI bootcamp] Day 12: Personal Diary App](https://growgrow.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/media/blog_images/4571735986511_.pic.jpg)

Comments
Please log in to leave a comment.
No comments yet.